Diabetic retinopathy is a disease that affects diabetic people and eventually leads to blurry, distorted vision and blindness. When people suffer from diabetes they may often have unstable glucose levels and they are prone to circulation problems in the back of the eye, known as the retina. The retina is a very sensitive part of the eye that is responsible for interpreting the images that you see and then transmitting these images to the brain. In the case that someone is diabetic they may experience a restriction on the flow of blood through the vessels within the retina. When this restriction occurs swelling, bleeding and even hemorrhaging may result. Aside from the threat of blood, sometimes fluid can collect under the retina-this problem is known as macular edema.
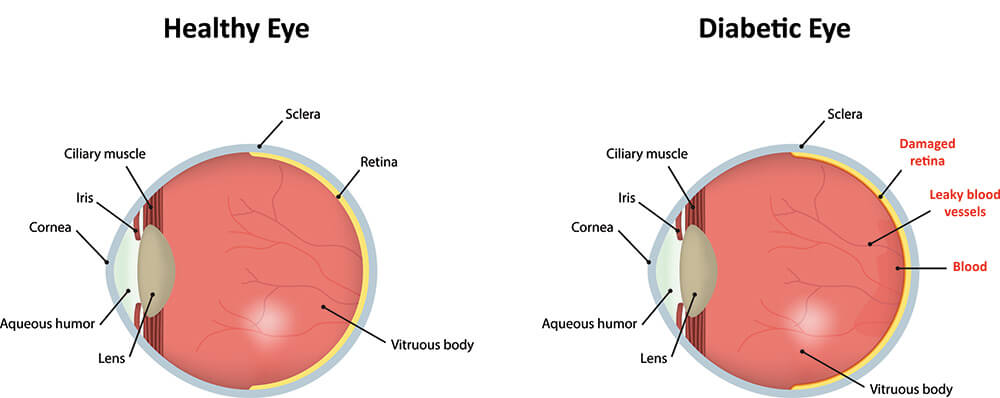
Many diabetic patients can have diabetic retinopathy without knowing it. Usually, there is no pain and no outward sign. Over time, you may notice gradual blurring or some vision loss. Symptoms may come and go. If diabetic retinopathy is severe, you may have clouded vision or blindness. You should have regular eye exams to help your doctor detect changes in your eyes before your vision is damaged. Treatment may help slow the progression of diabetic retinopathy and sometimes can restore lost vision. Your treatment depends on your condition, but may include frequent exams to monitor your condition, laser treatment, surgery or other procedures.
If you or a family member have diabetes, be sure to schedule a comprehensive eye examination to protect your vision. The doctors at Texas Eye Institute are experienced Texas retina doctors that can provide you with expert retina care in Houston. If you are diabetic contact us today! The proper diagnosis of Diabetic Retinopathy is made during a routine eye examination by directly observing the Retina through a dilate pupil but often requires further testing with Flourescein Angiography and Ocular Coherence Tomography (OCT).
It is very common that diabetic retinopathy can be found during routine eye exams at one of our Houston eye care locations. As previously stated, the Texas Eye Institute diagnosis of Diabetic Retinopathy is made during a routine eye examination by directly observing the retina through a dilate pupil but often requires further testing with Flourescein Angiography and Ocular Coherence Tomography (OCT).
“Nearly half of people with diabetes have some degree of diabetic retinopathy, a complication of diabetes that can result in blindness. After 20 years with diabetes, most patients have diabetic retinopathy. Treatment depends on the severity of the condition.” (quote from MAYO CLINIC)
Treating diabetic retinopathy requires a skilled retina surgeon for both careful evaluation. When changes are found there are some useful treatments depending on the nature and severity of the Diabetic Retinopathy. These include: Laser Treatment, Therapeutic Injections of Avastin and Lucentis, and if a hemmorhage has occured into the eye, Vitrectomy or sugical removal of the Vitreous.
There are two types of laser treatment. The first is known as Panretinal Photocoagulation (PRP) and it consists of laser spots being burned into a wide area across the the retina tissue to help with the decrease the retina’s need for oxygen. For this surgery the patient’s eyes are dilated and numbed. The doctor than focuses the laser on the appropriate locations of the retina and places the laser spots. Sometimes the outer vision of one’s eye is destroyed but the treatment helps save the crucial part center part of one’s vision. The patient will experience light flashes. Since a laser is used the patient will experience some discomfort but healing time is quick although a driver for the trip home is required.
The second type of laser treatment for diabetic retinopathy is Focal Laser Photocoagulation. During this procedure the blood vessels of the eye are sealed and shrunken. This procedure feels the same as the first laser treatment, and the patient is given mild numbing drops. This is performed in earlier stages of diabetic retinopathy in order to eliminate leaky blood vessels.
Vitrectomy is a different kind of retina surgical procedure that removes the vitreous so your surgeon can repair the damaged portion of your eye. Once the defect is repaired the surgeon then replaces the emptied cavity with a gas bubble. Since gas rises and the macula and retina are at the back of the eye, recovering patients must remain facedown in order for the gas bubble to effectively apply pressure to the area in need of healing, allowing the macula or retina to re-bond to the eye wall and a new vitreous to eventually replace the gas bubble.Although a vitrectomy is a relatively painless procedure with a strong, successful track record in improving vision, the recovery from vitrectomy is often more challenging because patients must contend with the monotony, stress and discomfort of a 23-hour-a-day facedown-postoperative position. Most vitreo-retinal ophthalmologists agree that a vitrectomy is most successful when patients fully comply with facedown recovery instructions.
Page Topics Include: Houston retina surgeons, diabetes and the eye, diabetic retinopathy, vitrectomy in houston, experienced retina doctors in Houston, diagnosing diabetic retinopathy.
Texas Eye Institute is proud to provide five convenient locations for your eye care needs. Visit one of our convenient locations in Angleton, Sugarland, Southwest Houston, Katy, or Southeast Houston to see why the Texas Eye Institute is the best choice to care for your vision. Need LASIK in Houston? What about a comprehensive eye exam in Sugarland? See our locations page to find our practice nearest you!









